3D Printing also known as additive manufacturing is the process of taking a 3D CAD (Computer Aided Design) file and turning it into a 3D solid object. The making of a 3D printed object is accomplished by using additive processes. An additive process is where an object is produced by laying down succeeding layers of material on top of each other up until the whole object is formed. Every layer is basically a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section taken from the CAD model.
How does 3D printing work?
The first stage of 3D printing is to obtain the 3D CAD data for the part you want to print. The CAD data could be created in a 3D modelling program such as SolidWorks or a 3D scanning of the object you want to print. The 3D scanning produces a 3D CAD duplicate of the scanned object.
The 3D CAD file then needs to be prepared for printing; this is done by slicing the CAD model horizontally into generally 0.1mm thick layers. The layer thickness can be altered depending on the finish required. As a smaller layer thickness will give you a model with more layers and a smoother surface finish. A greater layer thickness will produce a model with less layers and a reduced surface finish. With the slice file uploaded to the 3D printer the model can be printed layer by layer.
Processes and technologies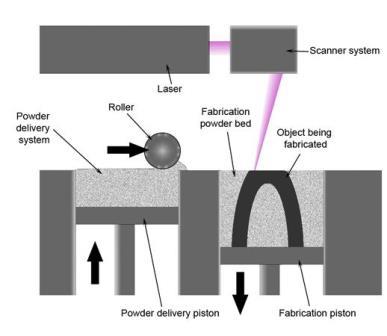
With all 3D printers using additive manufacturing there are several different techniques to achieve this. The main three used are, Selective laser sintering (SLS), fused deposition modelling (FDM) and stereolithography (SLA).
FDM is an extrusion based printer, so the material is extruded out layer by layer. This is the most common type of household/desktop 3D printer. SLS works by using a laser to fuse together a powered material one layer at a time with the laser aiming at the points defined in the slice file. SLA models are produced similarly to SLS but using a photo reactive UV resin and a UV laser.
Future
It is predicted that the future of 3D printing will change the entire market place. With 3D printers already able to print in colour and various materials already exist and this will carry on improving to the point where functional products can be produced by the end user. This reduces the need to purchase the finished product from a manufacturer or corporation.
With effects on customization, energy use, product availability, art, medicine, sciences and construction, 3D printing has the potential to alter the manufacturing world as we know it.